Inspection Tools: A Guide to the Tools Inspectors Use in Their Daily Work
Inspection tools help inspectors collect the data they need to ensure the proper maintenance of the assets they're inspecting—Read this guide for an overview of the different types of inspection tools they use.
Inspection tools are essential for gathering critical data that ensures the safety, efficiency, and longevity of industrial and mechanical systems. These tools enable inspectors to assess the condition of equipment, identify potential issues, and make informed decisions about maintenance and repairs.
The data collected can vary widely, including visual, thermal, or thickness measurements. The specific type of data required for an inspection depends on the asset being inspected and the inspection's objectives, which in turn determines the tools needed for the job.
Once data is gathered, inspectors analyze it to understand the current state of the asset and decide if any maintenance or intervention is necessary.
Inspection Tools vs. Inspection Equipment
In this article, inspection tools refer to the instruments and devices used by inspectors to collect data directly. For example, a thickness-measuring sensor used to evaluate the wall of a coke drum or a drone equipped with a camera to gather visual data from hard-to-reach areas.
Inspection equipment, on the other hand, includes everything that supports the inspection process, such as toolbelts, scaffolding, ropes, or other aids that allow inspectors to access and collect data more effectively.
[Related read: Confined Space Equipment: A Guide]
Whether it's a large industrial boiler or a residential HVAC system, the fundamental process remains the same:
- Inspectors collect data using inspection tools
- They analyze the data based on industry-specific standards
- Maintenance teams then determine the next steps based on their findings
While the concept is simple, the range of tools available is vast, often categorized by the type of data they capture or the environment in which they operate.
For instance, robotics solutions may be grouped by whether they are aerial, ground-based, or submersible rather than by the type of data they collect. This is because a single robot can be equipped with multiple sensors, allowing it to gather various types of data depending on the task at hand.
Now, let’s take a closer look at the different types of inspection tools commonly used in the field.
Â
Cameras and Other Visual Data Collection Tools
Visual data is one of the most frequently collected types during inspections. Cameras are the go-to tool for capturing this data, but not all cameras are suitable for every inspection. The choice of camera should depend on the quality and clarity of images required for the task.
Here are some common visual data collection tools used in inspections:
- Digital cameras: Available in various qualities and prices, digital cameras are ideal for capturing high-resolution images. Factors like low-light performance and color accuracy may influence the selection.
- Borescopes: These flexible tubes with lenses allow inspectors to see into tight or inaccessible spaces, making them invaluable for internal inspections.
- Video and digital microscopes: These tools magnify small details, helping inspectors detect minute defects or wear that might be missed by the naked eye.
- Videoscopes: Similar to borescopes, videoscopes have a built-in camera at the tip, enabling remote viewing of internal structures.
- CCTV: Used primarily in sewer and pipe inspections, CCTV allows for real-time video monitoring of underground systems.
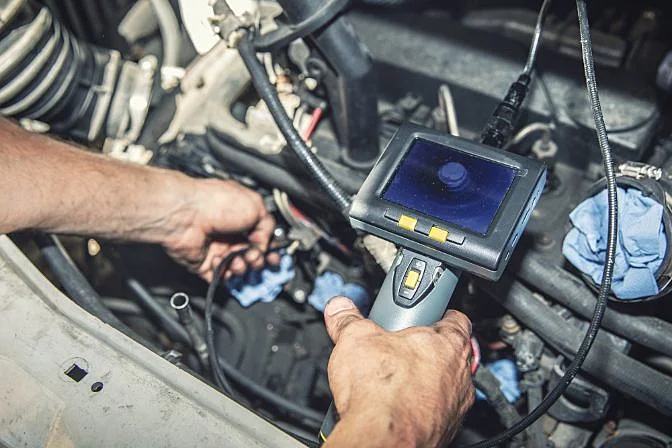 A borescope being used to inspect a car engine
A borescope being used to inspect a car engine
Other NDT Sensors and Testing Methods
While visual data is common, many inspections require additional data types. Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) methods and specialized sensors are often used to gather this information.
Ropes and Drones Case Study
A great example of how multiple tools and NDT methods can be combined is the inspection conducted by Premium Inspection & Testing in Louisiana. They used drones and rope access to inspect a coke drum without building scaffolding, saving their client $250,000 in the process.
Here’s how they did it:
1. Visual data collected by drone
Using Flyability’s Elios 2 drone, they first captured visual data inside the coker to identify areas of concern.
2. Corrosion and other data collected via rope access
Inspectors then used rope access to perform detailed tests, including 3D scanning, phased array testing, and liquid penetrant testing to check for surface defects and corrosion.
This case highlights the importance of combining different tools and methods to gather comprehensive data efficiently and safely.
NDT Sensors and Testing Methods
Some examples of NDT methods include:
- Thermal sensors: Used to detect heat loss or abnormal temperature distributions.
- Ultrasonic sensors: Help identify internal flaws using sound waves.
- Radiography: Uses X-rays or gamma rays to detect material imperfections.
- Eddy current testing: Measures electrical currents to find surface and near-surface defects.
These methods are vital for ensuring the integrity and safety of critical infrastructure and machinery.
Robots
Robots are increasingly being used in inspection tasks due to their ability to access dangerous or hard-to-reach areas. There are three main categories of robotic solutions used in inspections:
- Drones / Aerial Robotic Solutions
- Ground-Based Robotic Solutions
- Submersible / Underwater Robotic Solutions
Drones / Aerial Solutions
Drones have become a popular tool for Remote Visual Inspection (RVI), allowing inspectors to collect data from locations that would otherwise be difficult or unsafe to access. They can also be equipped with thermal or other sensors to collect additional data types.
Why use RVI tools?
There are several key benefits to using drones and other robots for inspections:
- Safety: Reduces the risk of human exposure to hazardous environments.
- Savings: Can significantly cut down on costs associated with scaffolding, labor, and downtime.
- Reduced downtimes: Speeds up the inspection process, minimizing operational disruptions.
Indoor vs. Outdoor Drones
Indoor drones, like the Flyability Elios 3, are designed to navigate confined spaces, while outdoor drones, such as the DJI Matrice 300, are built for open-air environments.
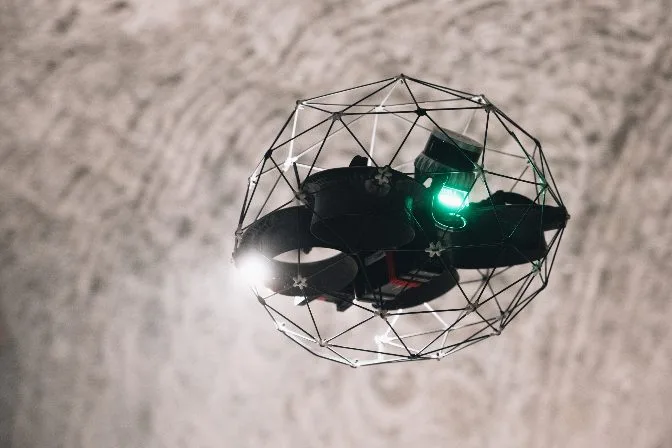 Flyability’s Elios 3, an indoor drone for confined space inspections
Flyability’s Elios 3, an indoor drone for confined space inspections
 DJI's Matrice 300, an outdoor drone used in inspections
DJI's Matrice 300, an outdoor drone used in inspections
Ground-Based Robotic Solutions
Ground-based robots are another form of RVI tool that can be used in a variety of inspection scenarios. Some examples include:
Inuktun MaggHD
 The Inuktun MaggHD is a magnetic crawler used for remote visual inspections in hazardous areas.
The Inuktun MaggHD is a magnetic crawler used for remote visual inspections in hazardous areas.
Deep Trekker DT320
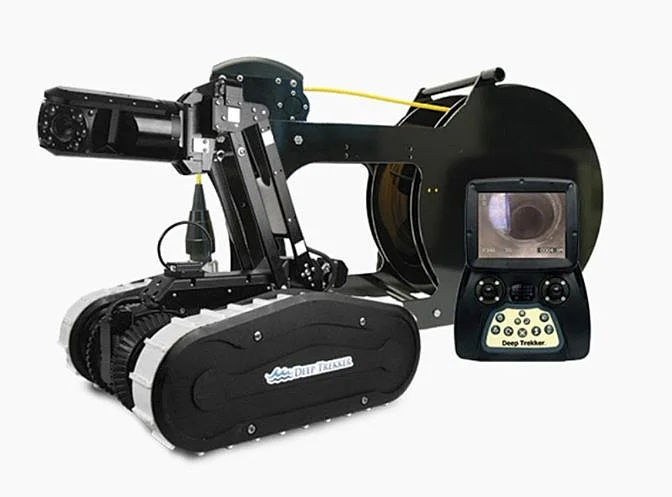 The Deep Trekker DT320 is ideal for inspecting pipes and small spaces where manual access is limited.
The Deep Trekker DT320 is ideal for inspecting pipes and small spaces where manual access is limited.
Inuktun Versatrax 150
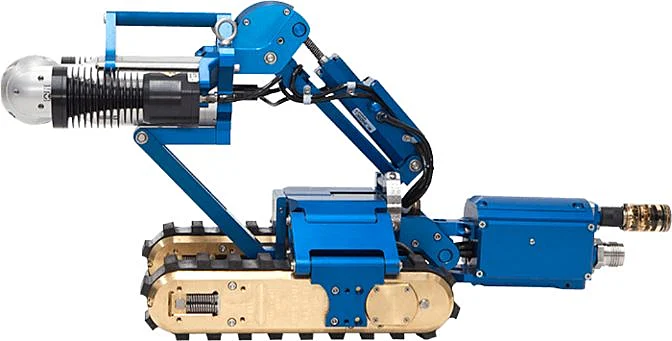 The Inuktun Versatrax 150 is a long-range inspection system used for tanks and wastewater infrastructure.
The Inuktun Versatrax 150 is a long-range inspection system used for tanks and wastewater infrastructure.
Submersible Robots
Submersible robots are also gaining popularity in the inspection industry, especially for underwater or liquid-filled environments. These robots reduce the risks associated with diving operations and can access areas that are otherwise unreachable.
MASKI+
The Maski+ remotely operated vehicle is used by HydroQuebec to inspect hydro dams in turbulent or deep water conditions.
INTERO TANK EXPLORER
The Intero Tank Explorer is an intrinsically safe robot used in petrochemical storage tanks. It can inspect tank walls while the tank is still in operation, detecting thickness inconsistencies and providing real-time imaging.
Recent Advances in Robotics
Future inspections will benefit from a wider range of robotic tools, including advanced NDT sensors. For example, robot-mounted ultrasonic testing tools are already being used in various industries. Additionally, new robots are being developed to inspect hazardous or inaccessible areas, such as aging sewage systems. Some of these robots even come equipped with tools to fix the defects they identify, such as water-jet cutters and UV-curable patches.
Measuring Devices
Measuring devices are essential for collecting precise data about the dimensions of objects or structures. These tools range from simple hand-held calipers to advanced digital gauges. For example, calipers are widely used for measuring depth, length, and internal or external dimensions of components.
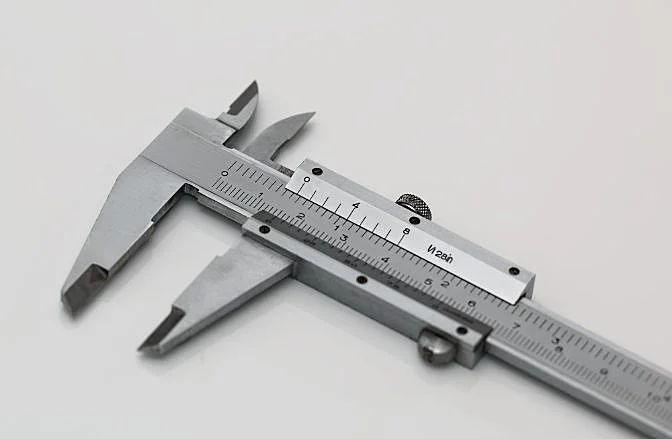
Common measuring devices include:
- Engineering Square: Helps determine perpendicularity and draw straight lines.
- Protractors: Measure angles between surfaces.
- Levels: Determine the inclination of a surface.
- Calipers: Used for precise linear measurements.
- Gages: Compare an object to a standard size for measurement.
- Micrometer: Measures very small distances with high precision.
Inspection Software
As the volume of data collected during inspections increases, managing and analyzing this data becomes a growing challenge. That’s where inspection software comes into play. Innovations in data collection and management are transforming the way inspectors work.
Improved Data Collection Software
Software like Flyability Inspector 3.0 now offers 3D modeling capabilities, allowing inspectors to create quick models of the assets they’re inspecting and pinpoint defects with greater accuracy.
Data Management Tools
New-generation software solutions are capable of processing vast amounts of data more efficiently. With the integration of AI and machine learning, these tools can quickly analyze data and provide actionable insights. For instance, sewer inspection software automatically identifies potential defects from uploaded images, streamlining the inspection process.
Whether through innovation or refinement, every advancement in inspection software contributes to safer and more efficient inspections for everyone involved.
Titanium Banjo Bolts,Titanium Banjo Screw,Titanium Banjo Single Bolt,Titanium Banjo Screw Bolts
Baoji Qiyuexin Metal Material Co., Ltd. , https://www.qyxtitanium.com